A tool for characterization of cast iron melt (CE-Meter)TEC-21
A "must" for thin-walled cast iron, complicated shapes, avoiding chilled layers, and high function materials.

Feature
Newly added functions
- a) Estimation of nodularity(SG%)
- b) chill
- c) ASTM Flake graphite size
- d) inoculant selection
- e) shrink
All the values of a) to e) can be obtained within 3 to 4 minutes after sample pouring.
Purpose of development of TEC-21
Quality control on the melting floor
Conventional CE-meters only determine chemical compositions and are unable to respond to advanced level of such technical requirements as thin-walled castings, complicated shapes, necessity of avoiding hard layers, or materials for high functions. This equipment was developed as a quality control tool on the melting floor that will greatly help production of castings for high technical requirements.

cooling curve for melt quality characterization in relation to phase diagram

a cooling curve and characteristic values
17characteristic values in a cooling curve
| 1) primary temperature (liquidus) | ℓL |
| 2) eutectic solidification temperature (eutectic point) | E |
| 3) primary solidification range | LC |
| 4) solidification range | LE |
| 5) primary solidification time | ℓ |
| 6) eutectic solidification time | e |
| 7) total solidification time | s |
| 8) primary solidification temperature gradient | tanθ |
| 9) primary solidification time ratio | ℓ/e |
| 10) undercooling |
UC=E-C |
| 11) undercooling point | C |
| 12) undercooling area | A |
| 13) eutectic solidification area | B |
| 14) pouring temperature | PT |
| 15) time from primary to eutectic point | ℓe-1 |
| 16) time from undercooling point to eutectic point | CE |
| 17) time from eutectic point to solidification end | EG |
1) Reading off CE value (L)
When molten metal is cooled and solidified, there is always a solidification point or starting temperature of solidification. Solidification temperature of a cast iron melt is dependent on its chemical composition. From starting temperature of solidification, CE value (Carbon Equivalent) of the melt can be determined. There are several different definition of CE value: C+ (1/3)Si, C+(1/3)Si+(1/3)P, C+(1/4)Si+(1/2)P, or C+0.3Si+0.3P. By examining quality control charts fitting to the conditions of your plant, you may be able to find out if you can use the CE value table of your CE-meter catalogue without correction, or you need to make some corrections to it. Generally speaking, the amount of necessary correction is not too large.
2) Reading off eutectic point (E)
A cast iron melt has its solidification end point or eutectic solidification temperature as well as solidification start point. Among the two major alloying elements of cast iron melt C and Si, the latter has a large influence on change of eutectic temperature, where eutectic temperature is raised by increased Si content. Thus Si % can be estimated from the eutectic temperature. Knowledge of eutectic temperature can be utilized for other purposes such as estimation of chill depth or shrinkage. Thus it can be said that eutectic temperature and primary solidification temperature are the two most important features of a cooling curve.
3) Reading off solidification temperature range (LE)
The temperature difference between the primary and eutectic solidification is called solidification temperature range LE. From this LE value of the melt, C% of the melt can be determined and mechanical properties of the castings from the melt such as strength or hardness can be estimated. .......This applies to irons without Tellurium.
4) Reading off undercooling(UC)
The phenomena of undercooling are observed more or less at primary and eutectic solidification. Undercooling appears when the balance between cooling rate of the melt and growth velocity of iron crystal is broken. Degree of undercooling (UC) has a close relation with the tendency of chill formation. Generally speaking, a large undercooling is accompanied by deep chilling and severe segregation. Growth rate of graphite in cast iron is said to be proportional to square of degree of undercooling. Therefore, a small undercooling causes slow growth, and hence, thick graphite with large layer distances. A large undercooling enhances growth of primary dendritic austenite and reduces amount of eutectic cell formation in the interdendritic area.
5) Reading off time of passing the solidification range (time ratio of ℓ and e)
Cast iron characteristics are also estimated by examining the time from the primary solidification through undercooling and to eutectic solidification. Consider the ratio between the time from primary to undercooling (primary solidification time ℓ) and the time from undercooling to eutectic solidification (eutectic solidification time e). Melt quality can be largely different between those with a large ratio and those with a small ratio, even when the total time is the same. Generally speaking, melts with a short primary solidification time and long eutectic solidification time are favored.
6) Reading off time from eutectic point to solidification end (inoculation effect)(EG)
A long time from the start of eutectic to the end of solidification (the range EG) indicates a good inoculation effect. .....graphite shape, eutectic cell number, graphite distribution.
7) Effects of soluble impurity in melt on cooling curves
Effect of 1% alloying element on solidification temperature of hypo-eutectic cast iron.(Results of three tests were averaged.)
| alloying element | change in primary liquidus temperature, °F |
Change in maximum eutectic temperature ,°F |
|---|---|---|
| Cr (Chromium) |
5 | -10 |
| Mo (Molybdenum) |
-2 | -18 |
| Nl |
-3 | +6 |
| Cu |
-5 | +5 |
| Mn | -5 | -15 |
8) Difference between a cupola melt and electric furnace melt with the same CE value Differences:
- 1) Cupola melt exhibits less undercooling.
- 2) Cupola melt has shorter ℓ and longer e.
- 3) Cupola melt exhibits better inoculation effect (Si%).
- 4) Cupola melt is better in chill tendency and shrinkage tendency.
Set up of the apparatus

Technical support
Off-set setting
We can offer assistance to preparation of calibration lines (to be charged).
Free rental for demonstration
Free rental with a cup stand (two~three days).
Technical note
A booklet is provided describing details of countermeasures.
Temperature sensor
Temperature calibration and paper preparation after ISO standard (to be paid).
Maintenance
Free maintenance for the initial one year. Paid maintenance after the initial period. Cost of repair of physical damages by accident must be paid by the customer, even though it may be within the period of free guarantee.
Specification [ TEC-21 ]
| Outside dimension |
H440 × W590 × D175 mm |
|---|---|
| Monitor | 21 inch touch panel (supersonic type) |
| OS | Windows Embedded |
| Storage period | Three years |
| Power source | AC 100 to 240 V |
| Temperature convertor | JIS-K |
| measurement range | 0 - 1370 |
| Interface | USB×1, VGA×1, RS232×1 LAN×1(option) |
| Cup stand | two sets (5m) |
| Weight | 15 kg |

 SG Cup P,QConsumable for chemical analysis of the cast iron molten metal
SG Cup P,QConsumable for chemical analysis of the cast iron molten metal SG Cup A(silica tube)Consumable for a tool for characterization of cast iron melt
SG Cup A(silica tube)Consumable for a tool for characterization of cast iron melt  Chill-CUPConsumable for a tool for characterization of cast iron melt
Chill-CUPConsumable for a tool for characterization of cast iron melt TEC-21A tool for characterization of cast iron melt (CE-Meter)
TEC-21A tool for characterization of cast iron melt (CE-Meter)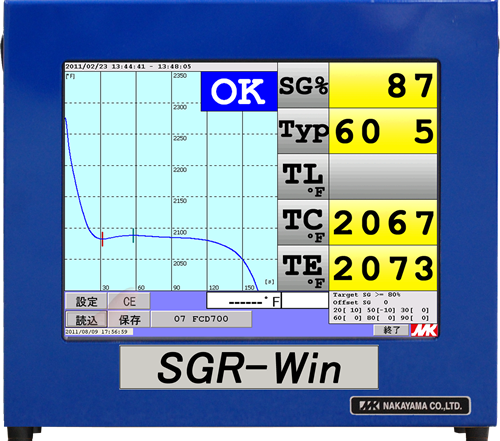 QCR-winThermal Analysis (CE-meter) / Windows Edition
QCR-winThermal Analysis (CE-meter) / Windows Edition QCR-D’s ICT-compatible Thermal Analysis (CE-meter)
QCR-D’s ICT-compatible Thermal Analysis (CE-meter) QCR-nanoThermal Analysis(CE-meter)
QCR-nanoThermal Analysis(CE-meter)  EZASimplified Thermal Analysis
EZASimplified Thermal Analysis 
